A S Ganeshan - Associate Vice President, Domestic Sales & Marketing, Jindal Aluminium

In the realm of contemporary architecture, engineered aluminium has emerged as a cornerstone of innovative design and structural ingenuity. This versatile material, celebrated for its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio and sleek aesthetic, is transforming skylines and redefining the boundaries of architectural possibility.
Engineered aluminium’s impact extends beyond its visual appeal; it plays a crucial role in advancing sustainable building practices. Its high recyclability and energy-efficient properties contribute to reducing the carbon footprint of modern constructions, aligning with global efforts towards eco-friendly development. Moreover, aluminium’s durability and low maintenance requirements ensure the longevity and cost-effectiveness of buildings, making it an economically viable solution in the long run. As we explore the marvels of engineered aluminium in contemporary design, we uncover a material that not only shapes our architectural landscapes but also paves the way for a more sustainable and innovative future.
Advantages of Engineered Aluminium in Architectural Applications
One of aluminium’s key benefits is its remarkable strength relative to its weight. This makes it ideal for structures that must support heavy loads without the burden of additional weight, making it a go-to material for tall buildings, bridges, and other large-scale constructions.Furthermore, aluminium is one of the most sustainable materials in the architectural industry. It is 100% recyclable and can be reused indefinitely without any loss of quality, a characteristic that is rare among other materials. Its durability also ensures that buildings made with aluminium have longer lifespans and require less maintenance, thereby reducing the environmental impact over time.
Aluminium’s high fire resistance is a significant yet often overlooked benefit. As a non-combustible material, it does not burn or decompose when exposed to fire, making it a safe and robust option for buildings that must comply with stringent fire safety regulations.
Aluminium’s remarkable design versatility and its malleability allow architects to craft customised shapes and sizes. Being lightweight yet incredibly strong, makes aluminium an excellent choice for constructing high-rise buildings.
A S Ganeshan
Innovative Applications of Aluminium in Contemporary Architecture
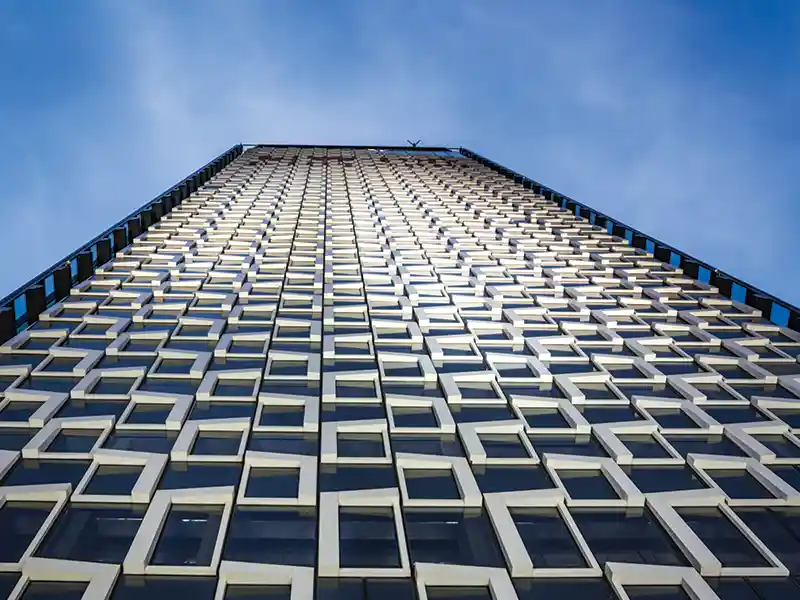
Aluminium Facades
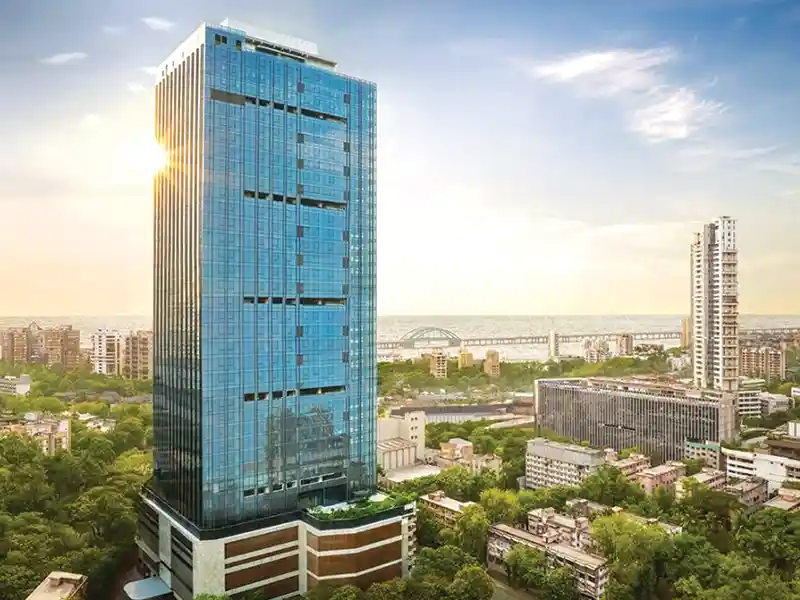
Aluminium is an adaptable material with numerous applications in contemporary architecture, particularly in building façades. These external surfaces are essential in shaping the overall visual appeal of a building. Engineered aluminium is frequently chosen for cladding façades because of its strength, light weight, and versatility.For panel cladding, aluminium provides a sleek, modern look and comes in various finishes such as brushed, anodised, and powder-coated, giving architects extensive design flexibility. Engineered aluminium is perfect for creating louver systems on façades. Louvers help regulate the amount of light and heat entering a building, and aluminium’s lightweight and durable nature makes it an ideal material for this purpose.
Aluminium Doors and Windows
Aluminium is a favoured material for doors and window frames in contemporary architecture due to its robustness, strength, and light weight. It is also highly resistant to corrosion and weathering, making it an ideal choice for enduring harsh environmental conditions.For frame construction, engineered aluminium is an excellent option. It is lightweight, easy to install, and provides outstanding strength and durability.
In terms of energy efficiency, aluminium can be used to create highly efficient doors and windows. When combined with double-glazed or triple-glazed glass and thermally broken aluminium frames, it significantly reduces energy transfer. This leads to lower energy costs and a decreased carbon footprint.
Aluminium Roofs
Engineered aluminium is a preferred material for modern roofing due to its light weight, durability, and adaptability. It is also resistant to corrosion and weathering, making it ideal for harsh environmental conditions.For standing seam roofing, aluminium offers excellent water resistance and accommodates thermal expansion and contraction with its interlocking raised seams. In shingle roofing, engineered aluminium replicates the look of traditional shingles while providing the benefits of metal, such as low maintenance and durability. Aluminium roofs can seamlessly integrate solar panels, offering a sustainable energy source and reducing long-term energy costs.
Aluminium Structural Applications
Aluminium is a favoured material in modern architecture for its strength, durability, and light weight. Its ability to resist corrosion and weathering makes it ideal for challenging environmental conditions.Aluminium is widely utilised for beams and columns in structural applications due to its superior strength relative to its weight. This property allows for extended spans with fewer supports, enhancing design flexibility and offering cost efficiencies. Aluminium is also a top choice for railings and stairs. Its light weight combined with high durability makes it suitable for areas with heavy foot traffic and frequent use.
Aluminium is ideal for awnings and canopies, providing effective shade and protection from the elements. Its robust yet lightweight nature ensures it can be easily supported by building structures while enduring harsh weather conditions.
Aluminium in Interior Design
Engineered aluminium is a sought-after material in contemporary interior design for its adaptability, stylish look, and long-lasting properties.Aluminium is often used for wall panels, which can be tailored to match the building’s aesthetic while serving both decorative and practical purposes.
In furniture design, aluminium offers a durable and lightweight option compared to traditional materials. It can be customised to complement the overall design of the space, making it suitable for a range of furnishings, from chairs to tables.