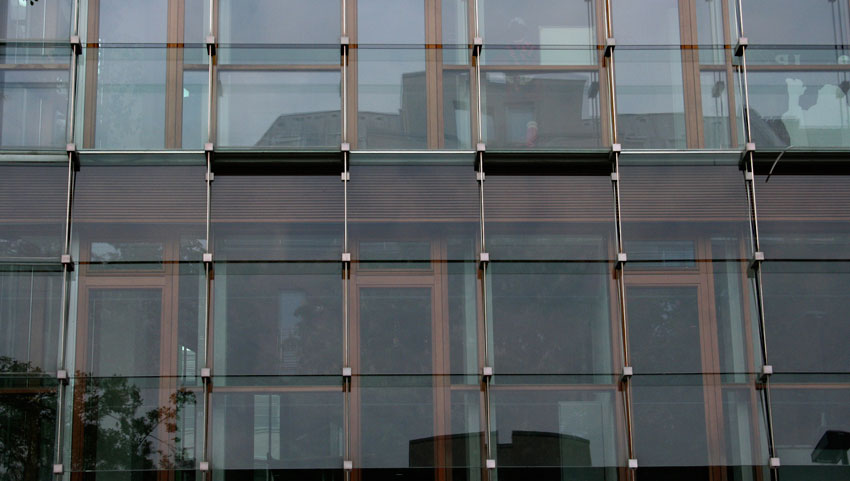
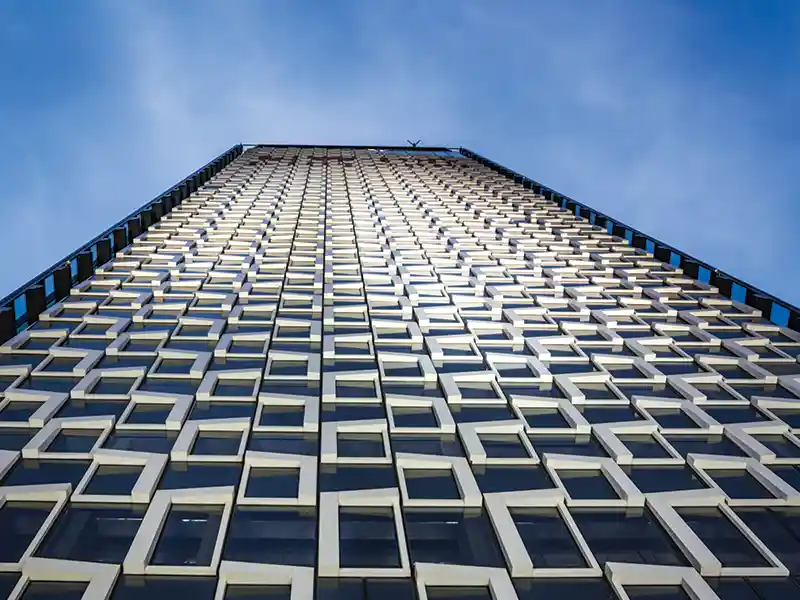
Twin-skin facade set-up encompassing thermal insulation timber elements and attached glass scales. Photo: Messe Düsseldorf
Twin-skin facade set-up encompassing thermal insulation timber elements and attached glass scales. Photo: Messe Düsseldorf
For some years now, glass has characterized modern architecture like no other material. Provided they are incorporated in an overall planning concept in line with their performance potential, glass materials not only characterize the appearance of facades but also make a decisive contribution to the energy efficiency of buildings. Based on experiences acquired with initial major projects involving a high percentage of glazing, the aspect of thermal protection in summer plays an especially important role today. Solar protection devices compensate for a disadvantage that often goes hand in hand with the transparency of glass architecture – much to the architects' regret – the undesirable build up of room temperature in summer. The use of the latest generation of coated solar protection glass can substantially reduce but not entirely avoid this effect. In winter, these solar gains are desirable by all means but in summer they can result in unpleasantly high air temperatures in building interiors.
Optimized Interplay

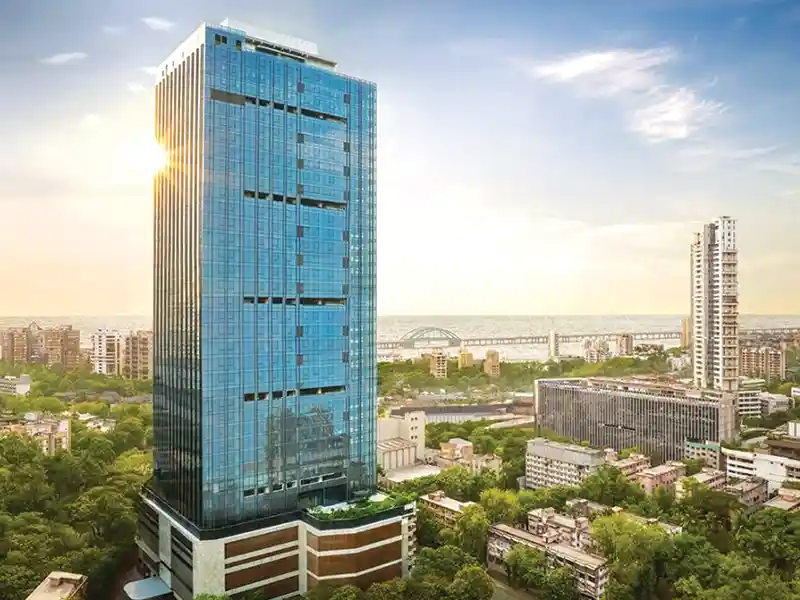
The glass facade of the Düsseldorf Stadttor is a twin-skin structure. The internal element facade with timber windows that can be opened and the outer glass skin in 12 mm TSG is set off by a 1m wide climate buffer. Air supply and exhaust openings are located at floor/ceiling level. Photo: Messe Düsseldorf
Experts principally agree that integral planning is required to efficiently leverage the energy and architectural potential of large-surface glazing in building skins. Planners and facade installers must, where possible, already cooperate in the development stages of a project. Only this multi-disciplinary collaboration and the consideration of the given climatic conditions at the location can ensure an optimised interplay of summer-time solar protection, ventilation and heating and/or cooling technologies.
New Opportunities through building-integrated PV
Building-integrated or to be more precise facade-integrated photovoltaics will also play an increasingly pivotal role in boosting energy efficiency in the future. Although numerous product solutions are already available in the market, installed systems can only be found in isolated cases. The reason for this is lack of consideration on the part of architects – something which solar industry experts discovered at the international Solar Summits congress. Even so PV modules can now be installed as systematically as conventional facade elements made from other materials.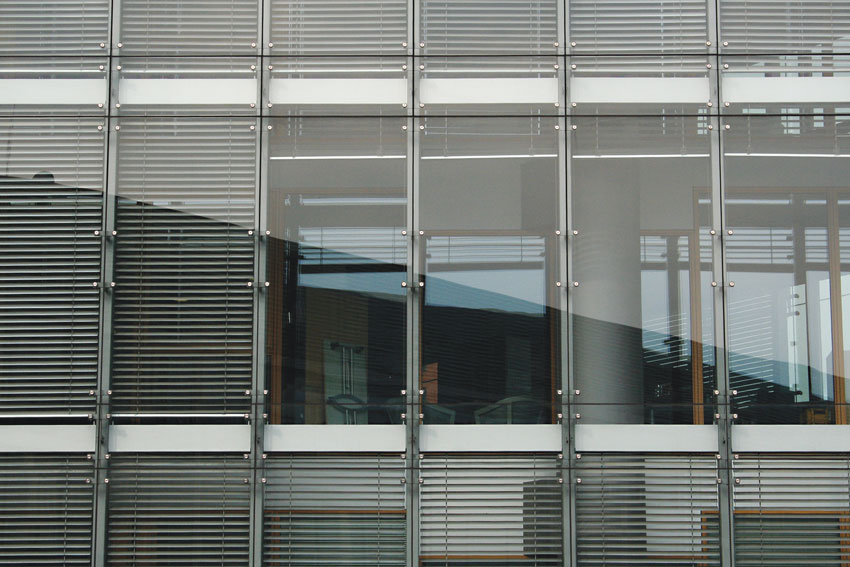 The TSG facade elements with bolt back assemblies at Düsseldorf's Stadttor are fitted with inside Venetian blinds on the office floors of the building. Photo: Messe Düsseldorf
The TSG facade elements with bolt back assemblies at Düsseldorf's Stadttor are fitted with inside Venetian blinds on the office floors of the building. Photo: Messe Düsseldorf

Even today PV elements featuring the latest thin-film technology can be ordered in various colours thereby providing more design freedom for facades. Prof. Eike Weber, Director of the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE, assumes that these new coloured solar cells will bring the desired breakthrough for building-integrated photovoltaics over the next few years. These cells, which were co-developed by the ISE, are based on completely different principles to the semi-conductor technology used so far. Since the technologies for their production are very similar to those already used in industrial glass processing, efficient manufacturing is possible. In addition to their use in new building integration-enabled photovolatics modules also have multiple applications in facade refurbishment.
The glass facade elements of the Capricorn Haus in Düsseldorf are multi-functional. Next to each countersash window with integral solar protection there is a 1.80 m high red glass panel. It conceals a facade module with cooling, heating and ventilation functions including heat recovery as well as lighting, sound dampening and interior acoustic elements. Photo: Messe Düsseldorf
Comprehensive Market Overview
Knowledge of the available glass products and their working principles is imperative for realising sustainable, energy-efficient glass architecture. Only by considering any glass versions that qualify for a building project can multi-disciplinary cooperation come up with holistic building concepts that live up to the high requirements made by both legislators and building owners. Glasstec the world's biggest trade fair for the glass provides an excellent overview of the latest developments in glass facades.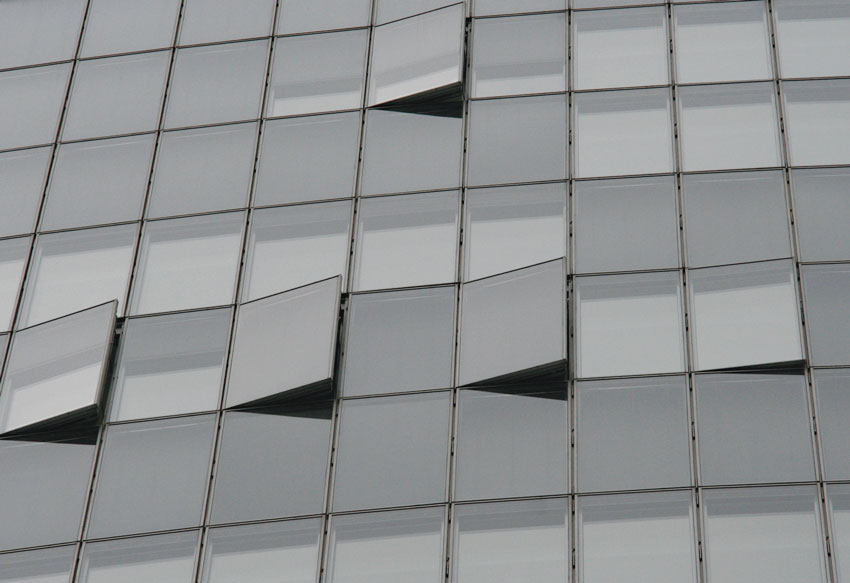 High energy efficiency of the glass facade does not exclude classic gap ventilation. Photo: Messe Düsseldorf
High energy efficiency of the glass facade does not exclude classic gap ventilation. Photo: Messe Düsseldorf