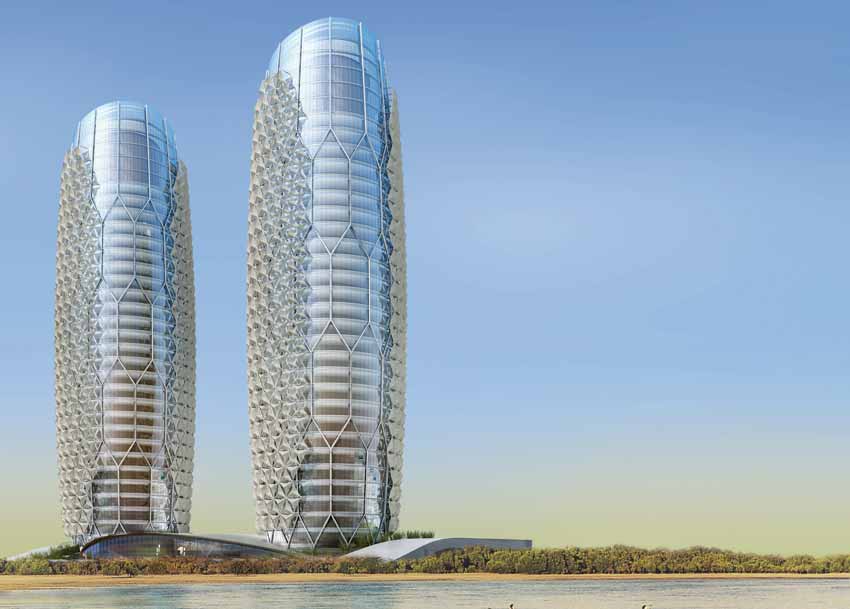
The design concept for Aedas's innovative competition winning design has been derived from an algorithmic composition, the Islamic principles of design, and has been supplemented by the application of a dynamic translucent 'Mashrabiya' which opens and closes in response to the movement of the sun, reducing solar gain on the building facade by up to 50%. The resulting composition seeks to create a building which is both culturally and environmentally responsive, reflecting the aspirations of the brief while also respecting the emergent Abu Dhabi 2030 Plan. The building is targeting a LEED Silver rating and expected to be completed by the beginning of 2012.
| Project at a Glance | |
| Project | : Abu Dhabi Investment Council headquarters |
| Type | : Commercial |
| Location | : Abu Dhabi, UAE |
| Client | : Abu Dhabi Investment Council |
| Architect and Lead Consultant | : Aedas Architects Ltd |
| Consultant/Structural Engineer | : Arup |
| Cost Consultant | : Davis Langdon LLP |
| Landscape Architect | : Townshend Landscape Architects |

Design Concept
The project's design concept is both culturally and environmentally appropriate and complies with the aspirations of the recently published 2030 Abu Dhabi Development Plan.The building design concept is based upon a desire to create a composition which will respect the prestigious nature of the Investment Council while also reflecting the underlying cultural tradition in a modern idiom, and responding to the prevailing environmental conditions. In response to the client's brief, Aedas's design approach for the buildings were influenced by three key drivers; inspiration from nature, sustainable design and the principles of Islamic architecture, a key aspect of which is geometric composition.
Geometry
Geometric composition has been a defining characteristic of Islamic architecture for centuries, the circle and rotation reflecting the concept of unification and unity evident in nature; an important concept in Islam and in the emerging science of biomimicry. For this project, a geometric pattern has been conceived, in order to provide a framework upon which the towers stand on adjacent sites. The resulting geometrical framework, when applied to the towers results in a parametrically based, i.e mathematically rationalised form, allowing the design to be developed with precision and accuracy.
Towers form
The starting point for the design was two cylindrical towers, a circle producing the most efficient form in terms of wall to floor area together with the maximum volume with minimum surface area. The geometry generated an articulated plan form to provide orientation, creating a front and a rear elevation. The form of the tower was sculpted around the core, narrower at the base and at the top, but broader around the intermediate floors. The crown of the tower was cut at an angle in order to maximise solar gain for roof-mounted photovoltaic's and sky gardens were introduced in the most heavily exposed southerly elevation to reduce solar gain while providing an amenity space for users.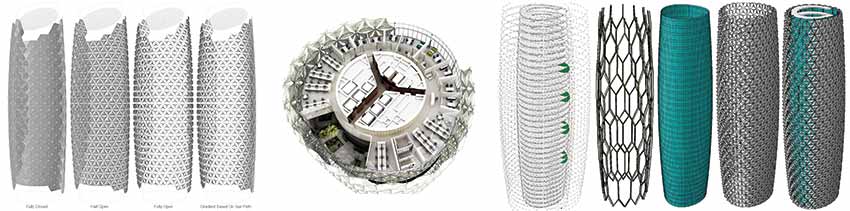
The towers provide circa 55,000sqm of flexible accommodation which can be arranged in open-plan or cellular configuration.
Structural System
A crystalline/honeycombed structure has been derived from the underlying geometry that provides highly efficient load paths and creates a structural solution which is at once stable, flexible and economical. The structural form also embodies a high degree of redundancy which would be very resilient if damaged. The Abu Dhabi Investment Council building superstructure is expressed on the external face of the building reflecting the underlying geometrical framework.The Dynamic Mashrabiya
A key feature of the design is the application of a diaphanous screen that envelopes the most exposed aspect of the building in the form of a dynamic 'Mashrabiya. The Mashrabiya screen solution has responded to the United Arab Emirates' aspiration to become a leader in the field of alternative energy, as evidenced by the recent Masdar initiative. Preliminary estimates suggest that the screen will result in a 25% reduction in the cooling load, thereby substantially reducing the carbon footprint of the Abu Dhabi Investment Council building towers.
Each Mashrabiya comprises an umbrella-like unit which opens and closes throughout the day in response to the sun's movements. Each Mashrabiya comprises a series of PTFE fabric mesh panels that are driven by a linear actuator. As each tower comprises circa 1,000 Mashrabiya units, so it has been estimated that the 'Mashrabiya' will achieve a 50% reduction in solar gain, a significant reduction in electrical energy consumption together with a reduction in total site CO2 emissions of over 1,750 tonnes per year.
Sky Gardens
In order to further reduce the potential for solar gain, the form has been sculpted to provide sky gardens in what would otherwise have become the most sensitive areas of the building. The sky gardens also provide visual relief for users of the building and an important amenity space for staff during the cooler months of the year.Roof Form
The sculptural form of the tops of the towers has been driven by a desire to take advantage of the sloping southerly aspect to apply a skin of photovoltaic cells whilst simultaneously maximising the more sheltered northerly aspect providing open views towards the sea.Basement Accommodation
There are two levels of basement, providing circa 37,500sqm of accommodation for parking, plant and back of house functions. The car-park will accommodate over 750 vehicles.Ground Floor and Podium Accommodation
The two towers are tied together by means of a podium block comprising circa 14,000sqm of accommodation, which provides controlled access to both towers. The podium block also contains a number of shared facilities including, cafeteria, prayer rooms and a lecture theatre while discrete access for VIP's is provided at podium level. The ground floor and podium block comprise a lightweight shell roof that has been derived from the same geometric composition as the towers. The roof is supported by a series of 'tree-column's' and the mezzanine accommodation within the podium area has been hung from the structure above.
Elevators
Each tower has been provided with 5 passenger lifts plus 2 VIP lifts and 2 service elevators. In order to ensure effective security of the building, staff using the basement car park access the towers by means of escalators via the ground floor.Sustainability Features
The building is targeting a LEED Silver rating and the following are among the measures to be adopted, in addition to the 'Dynamic Mashrabiya':- Installation of solar panels at podium level to generate hot water
- Reduction in water usage
- Use of materials that are regionally sourced
- Use of materials with a high recycled content
- Use of wood from forests which are certified in accordance with the Forest Stewardship Council's (FSC) Principles
Landscape
The design of the exterior landscaping reflects the geometrical composition of the building and comprises a variety of hard and soft treatments, together with a number of water features. The landscaping within the Sky Gardens comprises a more formal arrangement of boxed plants and seating areas. All landscaping will be irrigated using non-potable water and only water efficient species have been selected.Construction Technology
In order to achieve a fast-track programme, an enabling works contract was awarded following completion of the detailed design. The enabling works contract included construction of the water retaining basement perimeter together with the piling and basement blinding.The tower cores are being constructed using 'slip-form' technology which has allowed a continuous pouring sequence to be maintained. The superstructure of the towers comprises a steel structure with a sprayed fire-resistant coating. The tower floors comprise in-situ concrete slabs cast over 'Holorib' permanent shuttering spanning between radial steel beams.
Building Information Modelling [BIM] was implemented early in the project to ensure proper coordination of the principle interfaces. Key components, including the steel superstructure and the façade, have been simulated in BIM with fabrication cutting lists extracted directly from the digital 3D model and members manufactured and cut to size using CNC technology. Also the components including the steel superstructure and the façade have been installed using GPS surveying technology to manage the complex geometry and provide the levels of accuracy required.
The construction of the project is at an advanced stage and is expected to be completed by the beginning of 2012.















