In most of the developing villages / cities / towns and such other locations the problem of maintaining hygiene condition and elimination of foul smell of the toilets or water closet (abbreviated W.C.) in the rest rooms / comfort rooms has become a severe problem. Swatch Bharat aims at having rest rooms with or without toilet (RRWWT) in all the Indian villages, remote rural and such other places where there is no toilets and RRWWTs. However, it is to be noted that by just having a private toilet and a RRWT in each of the houses or public four to eight toilets and rest rooms RRWWTs in a village does not ensure hygienic condition. The toilets and the RRWWTs should be always kept clean and there should not be any foul smell. Generally the toilets / commodes/ sanitary wares / RRWWTs are cleaned by water, soapy water, detergent water, phenol, solid or liquid toilet cleaner and such other cleaners. However, it is to be noted that with or without the said type cleaners necessitates manual effort for the cleaning purpose.
Introduction
A house / residing place at any place necessarily will have a rest room with appropriate fixtures. However in some of the under developed countries there neither public RRWWTs nor private RRWWTs (rest rooms constructed within /attached to the dwelling place or constructed near to the dwelling place) are not constructed. Most of public or private RRWWTs, without maintenance will generally be unclean and unhygienic. This is mostly due to illiteracy or due to carelessness. However, to be healthy and to maintain healthy environment in and around the residence / the location, the RRWWTs with appropriate fixtures to be necessarily constructed with appropriate toilets and they should be kept in clean and good hygienic condition. It is observed that most of the toilets are manually cleaned. In the present article, possibility of eliminating the manual cleaning of the toilets by using modified flush tank system for the automatic cleaning the toilets to keep them in clean and hygienic condition is discussed.
Theory
A RRWWT / W.C. / toilet are the part and parcel of the residential building. Prior to the construction of the residence a drawing is made to get the approval of the government organisations. In this particular drawing the number, type and location of the toilets are shown.
Usually the different RRWWT fixture are, *Lavatory, *Indian type toilet / basin, *western toilet, *tank and piping for water, mug, bracket for keeping soap for hand washing and keeping cleaning material,* cleaning sweeper / toilet brush, *windows for ventilation *good door with latches and septic tank in villages or drainage pipe to connect the toilet to the city sewage pipes. In most of the urban residences / apartments, commodes (western toilets) are common in the rest rooms where as in rural residences Indian type (IT) / squat type are installed.
The western toilets (WT) are popular. Different types of WTs are available. The main features of WTs are that * a seating arrangement, * cover, * sitting cover *rat trap / “S”, “U”, “J”, or “P” shaped bend / syphon, *flusher with proper flush tank and flushing chain / push buttons / twist knobs, *embedded flush water way within the walls of the WT and *pipe to connect the bowl and the sewer pipe . They are designed either for designed for sitting or for squatting or a flush toilet designed for sitting and cistern; or a squat toilet, with water tank for flushing. Generally ceramic / vitreous ceramic was used to manufacture WTs. Due the availability of Hi-Tech plastic materials, now plastic WTs are manufactured and are made available in the market. However, most of the features are not much changed. The most important observations are that these are to be manually cleaned.
There are three styles of toilets, * The Wash- down style, * The Wash-out style and * The Reverse Bowl or Shelf Style. One side of the U conduit is has a hollow siphon tube longer than the water in the bowl is high. The siphon tube connects to the drain. The stagnant water in the bowl acts as a barrier to sewer gas coming out of the sewer through the drain, and also as a barrier for the waste matters and the rats. Sewer gas is vented through a separate vent pipe attached to the sewer line.
When a user flushes a toilet, the inlet of the syphon (in the old mechanism -flapper valve opens) in the flush tank gets opened and siphons the water from the flush tank quickly to WT`s bowl.
This rapid influx from the tank results in the swirling of the water within the bowl and fills the U-shaped inverted siphon tube mounted in the back of WT and facilitates the required siphon action. The siphon action quickly siphons all of the waste and water from the bowl down the drains. After flushing, the siphoning action stalls and the flush tank is refilled facilitating WT again ready for use.
The ballcock or float valve is often used to regulate the filling of the flush tank or cistern. When the fluid level drops, the float descends, levering the valve opening and allowing more fluid to enter. Once the float reached the ‘full’ position, the arm presses the valve shut again. These types of valves are found in almost all types of toilets. The valves are of two main designs, *the side-float design and *the concentric-float design. The side-float design has been used since over a hundred years. The concentric design is recent developed valve, but is gradually becoming more popular than the side-float design. The side-float design uses a float on the end of a lever to control the fill valve. The float is usually shaped like a ball, so the mechanism is called a ball-valve or a ballcock. The float was originally made from copper sheet, but it is now manufactured using plastic. The float is located to one side of the main valve tower at the end of a rod or arm. As the side-float rises, so does the side-float-arm. The arm connects to the valve that blocks the water flow into the flush tank, and thus maintains a constant level in the tank.
The siphon flush system (SFS), has been invented by Albert Giblin, uses a flush / storage tank. SFS is sometimes referred to as a valve less system, since no flapper type of valve is required. In SFS, the user presses a knob or valve opening mechanism, forcing the water up into the tank siphon passageway which then empties the water in the tank into the bowl. The advantage of a siphon over the flapper valve is that it has no sealing washers that can wear out and cause leaks, so it is favoured in places where there is a need to conserve water. The use of siphon flush system has the advantage of avoiding the waste of water by millions of litres as compared to the toilets with flapper valves. However, SFS are sometimes more difficult to operate than a flapper valve systems because SFS lever requires more torque than a flapper valve system.
Earlier systems, known as high suite combinations, used a high water head level (higher potential head) tank and were operated by pulling a chain hanging down from a lever attached to the tank. Modern close coupled water tank and bowl combinations is first referred to as low suite combinations. New versions have a good looking low level tank with a lever that the user can reach directly, or a close-coupled tank that is even lower down and is integrated with the bowl itself. In recent times the close coupled tank with improved and effective waterway design has become the popular. To conserve water dual flush toilets have been designed. In this type, dual flush system is installed to use either to flush comparatively less amount water or to flush a large amount of water. The dirty matter from the bowl of WT is washed out to the sewage conduit by flushing water.
Fluid power is an oldest subject and it includes fluid mechanics, fluid kinematics and fluid dynamics. In fluid mechanics the characteristics of stagnant fluid or fluid at rest is the most important part. By the by fluid may liquid / incompressible fluid or may be gaseous / compressible fluid. In WT`s water is used. Hence, it is better to know the characteristics of water at rest / stagnant water (SW). It is observed that the pressure intensity in SW varies in the vertical direction / plane. The pressure intensity increases along with the depth. The more the depths with respect to the water free surface level of SW, more will be the pressure intensity. However along the horizontal direction / horizontal plane, the pressure intensity will be always constant and its value will be same in all the directions.
Methodology
Let be there an ordinary rectangular cross section big tank with no opening and a small rectangular cross section tank with a small opening at its bottom. Let this big tank be filled with water up to a level of 3meters, measured w.r.t. to the bottom of the tank. If the water level is 3metres, the pressure head on the bottom surface will be 3metres of water. In the similar way if the small tank is filled with water up to 1.5metres, the pressure head at its bottom surface will be 1.5metres of water. It is observed that no water flows out from the opening of the small water tank when the small water tank with a small opening at its bottom surface is kept in the big water tank at a depth of 1.5 metres from the bottom of the big water tank.
This is due the high pressure head in the big tank acting at that water level. This fundamental fact is used to modify the flushing system of WT and to achieve automatic cleaning [7, 8 and 9].
Working of modified WT
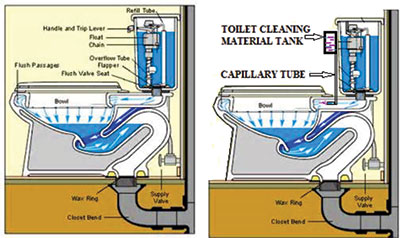
The proposed modification is simple. A small tank with opening at its bottom has to be fixed as shown in figure 02. This tank stores the liquid phenol and the free surface level of the phenol will be lower than the free surface level of the water in the flush tank. The opening of the small tank is connected to the water pipe of the flush tank (connecting the flush tank opening at the bottom and bowl of WT) with a capillary tube. The end of the capillary tube is bent at 900 so that its opening is along the direction of water flow from flush tank to the bowl.
Since the pressure head of phenol is less than the water head in the flush tank, though the capillary tube completely open, phenol will not flow out the capillary tube. It will flow only when the water flow starts in the flush tank bottom pipe. Hence, whenever the WT is flushed automatically phenol flows into the bowl along with the siphon water and cleans the whole bowl. As and when wate r flow stops, the flow of phenol also stops till the next flushing takes place.
Maintenance
Though the cleaning of modified flushing system of WT is automatic, it requires regular maintenance. Main maintenance is similar to that of maintaining the conventional manually cleaned WT. Ordinary toilet cleaning is done using a toilet brush. Various types of brush designs are available, some including a holder to enclose/cover the brush when it is not in use.
Now varieties of toilet cleaners – liquid or solid (chemical or herbal) – are available. WT can be cleaned by using these cleaners and the toilet brush or only the Hi – Tech toilet cleaners [10 and 11]. The flush tank, tube and the capillary tubes must be cleaned periodically.
Sometime clogging may occur. It is due to the flushing unsuitable items or too much toilet paper. Flushing of large amounts of hair should also be avoided. The clogging can also occur due to lime scale formation within the drain pipe, or by overloading the stool capacity of the toilet. Stool capacity varies among toilet designs and is based on the size of the drainage pipe, the capacity of the water tank, the velocity of a flush, and the method by which the water attempts to vacate the bowl of its contents. Sometimes, three to four flushes are required to prevent clogging. Partial clogging occurs when flushing a loaded toilet. In this water mixed with waste excrement overflows WT. However it depends on the bowl volume, flush tank capacity and severity of clogging. For this reason, rooms with flush toilets may be designed as wet rooms, with a second drain on the floor, and a shower head capable of reaching the whole floor area. Common means to remedy clogging include use of a toilet plunger, drain cleaner or a plumber’s snake [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6].
Conclusion
Toilets that used water were used in the Indus Valley Civilization. The cities of Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro had a flush toilet in almost every house, attached to a sophisticated sewage system. The modern system differs only a little bit. However all these are manually cleaned. The modified flushing system for the automatic cleaning WT cleans itself without any manual efforts. It is observed that the diameter of the capillary tube can be selected appropriately for saving the cleaner flowing into the bowl. This is achieved by calibration. If the capillary diameter is a higher gauge hypodermic needle can be fixed at the outlet opening of the capillary tube. Again calibration is necessary to determine the correct gauge number of the hypodermic needle. This modified flushing system can be conveniently installed in the Indian type toilets / squat toilets with flush tanks, in the lavatory sinks with flush tanks and in other such RRWWTs /toilets/sinks with flush tanks.
The modification of the flushing system of WC may increase the system cost no more than 0.2-0.4% of the total cost of WC installation and there will be comparatively savings in the toilet cleaner. The methodical experimentation will ensure the working the modified flushing system.
References
- www.toilet - repairs.com
- www.hindware.tradeindia.com
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flush_toilet
- www.parryware.in/Parryware. Bathroom Products., Bath Accessories India. Parry ware.
- www.neycer.in/ Neycer India Ltd. Home
- www.cera-india.com/CERA Sanitary ware - cera-india.com
- A K Jain, A book on Fluid Mechanics (including Hydraulic Machines), Khanna Publisher, New Delhi. 2008.
- Victor L. Streetor, E. Benjamin., A book on Fluid Mechanics., Wylie Publication., 1979 edition.
- Dr. D.S. Kumar, A book on Fluid Mechanics and fluid Power Engineering, S K Kataria & Sons. Delhi. Sixth Edition.,1998.
- https://www.amazon.com/Lysol-Power-Toilet-Cleaner-Value/...reviews/B006RG0S8K., Amazon.com: Customer Reviews: Lysol Power Toilet Bowl Cleaner ...
- https://www.housekeeping.about.com › ... › Bathroom Cleaning Tools., Five Best Toilet Cleaners - Housekeeping - About.com















