Buildings across the globe consume 60-70% of the total energy generated and are a major contributor to the greenhouse gases. The maximum share of this energy usage is in conditioning (heating or cooling) the building interiors. In India, which has a tropical climate, insulation of building envelope would result in major energy saving and minimizing the greenhouse gas emissions which would contribute to a green and sustainable development. This paper dwells on the various aspects of "Total Insulation" of building envelope that includes moisture insulation (waterproofing) and thermal insulation.
Introduction
It is estimated that across the total life-cycle of a building, the design and construction of a commercial building constitutes just 20-30% of the overall cost; the rest comprises operations and maintenance costs. Hence, it is important to actually consider how the high cost of operating can be reduced substantially.Today's modern buildings – marvels in terms of architecture and technology – have led to an adverse impact on the environment. Buildings are responsible for more than half of harmful greenhouse gas emissions in most major cities of the world.
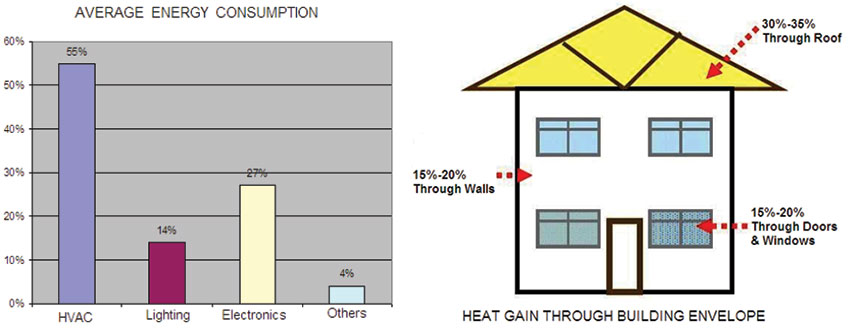
The maximum energy demand 50-70% in a building is for conditioning (heating or cooling) the interiors. This major energy demand in a building is due to "Building Envelope" which contributes to 60-75% of the heat gain/loss. Recognizing the need to save energy and minimize green house gases, efforts are being made to increase the awareness and importance of reducing energy loads in a building. Insulation of building envelope has become one of the key practices across the globe to effectively manage heat incidence in the buildings and save on the high energy cost.
For roofs, both LEED-India and GRIHA advocate over-deck insulation as against the conventional way of under-deck insulation; green credit points for building envelope insulation are credited for over-deck roof insulation.
In over-deck insulation, a thermal insulation with waterproofing is provided over the RCC as a barrier against direct solar heat on RCC roof slab. This prevents the RCC slab from heating up. The conventional method is under-deck thermal insulation by using methods like false ceiling or extruded polystyrene. However, its effectiveness is always a question since the thermal barrier is provided under the RCC roof slab. Some heat passes through the under-deck insulation and decreases the comfort level of the room. If the building is air-conditioned, this heat leakage increases the AC load. Hence it can safely be concluded that over deck insulation has its own advantages against under deck.
Building Envelope Insulation – A Holistic Approach
I. Roof Insulation (Over-Deck) This type of insulation has to take a composite approach to provide –- Thermal insulation
- Waterproofing and
- Slope built-up
Brick bat Coba

Advantages
- Provides Slope: This system provides an excellent slope for the water to drain away. As water does not accumulate and it has a certain capacity to absorb water, there is no leakage.
- Impose Dead Load: This system puts unnecessary dead load on the structure.
- Cracks Up: Brick bat coba cracks up due to temperature variation and movements due to thermal stresses. Once cracks appear, water travels below the coba and leakage starts. It is very difficult to trace the inlet point and repair it.
- Difficult to Dismantle: Some parts of the coba stick so well to the concrete that an attempt to dismantle the system may damage the slab.
Tar Felt / APP Membrane
This system uses layers of tar interspersed with various forms of reinforcements to hold the layer together and prevent cracking to provide impermeable layer between the water and the surface to be protected.
- Cheap
- Suitable for AC sheet roofing
- Not UV Resistant: Tar/Bitumen - the binder in the system disintegrates on contact with 'UV' radiation leading to biodegradation of reinforcement leading to collapse of the system.
- Debonding: Vapour trapped inside exerts vapour pressure resulting in debonding of the membrane.
Mud Phuska
In this conventional system of providing thermal insulation, a 10 cm layer of puddled clay mixed with grass straw is applied in slope on a sand-bitumen waterproofing layer. This layer is consolidated and plastered with 13 mm of cow-dung mortar. Tile bricks are laid flat on plastered surface and the joints are grouted with cement mortar.The Thermal and surface properties of mud phuska are as below Density = 1622 kg/m3 Thermal conductivity = 0.750 W/mK Specific heat capacity = 0.88 kJ/kg-K
[Reference: SP 41, Handbook on functional requirements of building (Other than industrial buildings), Part 1-4, Bureau of Indian Standard (1988)]
The traditional and conventional systems of waterproofing and thermal insulation in India worked well for ages to suit the Indian construction and economics. However, these systems do not have a long life and require frequent maintenance and also do not suit the complicated site dynamics of today's construction and do not offer insulation values to comply to ECBC norms.
Total Insulation Concept
To provide over-deck roof insulation that complies to ECBC requirements, a composite built-up is required which consists of a thermal insulation material with high "R-value", coupled with a suitable waterproofing and complete with a light weight material for the slope built-up for water run-off. A typical schematics of total insulation built-up would be as shown in the diagram below.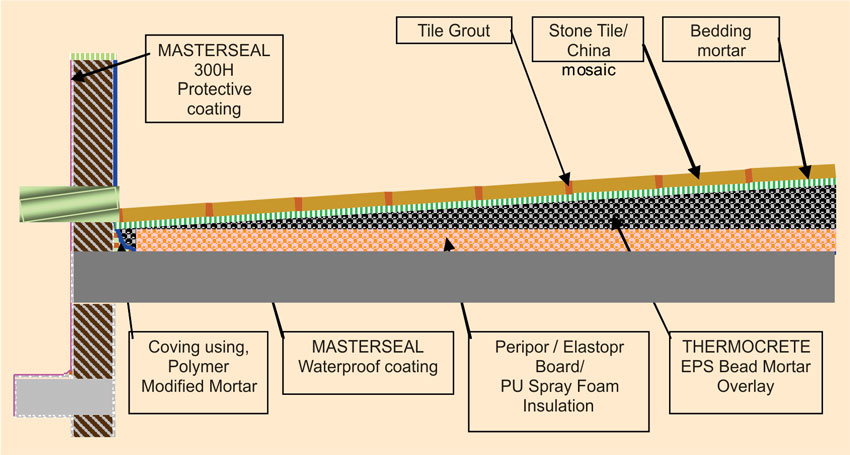
Roof Insulation Components
Waterproofing
- MASTERSEAL® 550 EL: Two-component, flexible, cementitious, polymer modified, brush-applied, water-proof coating can be applied directly on the concrete substrates and provides watertight sealing of pores and dormant cracks in the substrate.
- MASTERSEAL® HLM 5000R: Single component, moisture curing, liquid applied, modified polyurethane, Elastomeric water-proof membrane has >600% elongation.
- MASTERPREN® TPO: Single-ply, preformed, TPO water-proof membrane is a single-ply, water-proof membranes available in glass/polyester reinforced versions. MASTERPREN® TPO can be selected and designed on the basis of the roof overlay like green roof, podium, ballasted roof, metal deck. It is also capable of re-roofing the existing leaking roof without dismantling the existing system.
- CONIROOF®: Spray-applied, PU water-proof membranes consists of low-modulus PU membrane which is best in class for high elasticity and high adhesion capability which makes it perform on variety of substrates like natural stones, bricks, metal sheets, marine ply and even old/leaking bitumen membranes and PVC membranes.

- Peripor Board: The Water-resistant insulation
When building components are subject to pressure and moisture, the insulating materials used should absorb as little water as possible since water absorption has a significant detrimental effect on thermal insulation. Peripor Board has been developed specifically for such applications. It is a high-quality thermal insulation product with a water-resistant bead surface. This combination of properties greatly reduces water absorption and is thus suitable for use in the tropics. - Elastopor Board: Thermal Insulation PUR Board
Polyurethane Resin (PUR) based thermal insulation boards offer best in class insulation performance. Higher densities make the boards tough and can be used in trafficked system built-ups. Elastopor Boards are specially designed with skin layer on both faces, making it resistant to water ingress and long lasting.
- MASTERSEAL 755 SPF: Spray applied PU foam for thermal insulation is a two component system, spray applied at site. This allows spray application on complex substrate shapes and confined spaces, besides it lowers materials transportation cost.
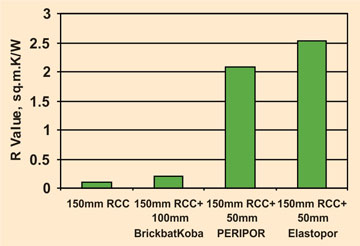
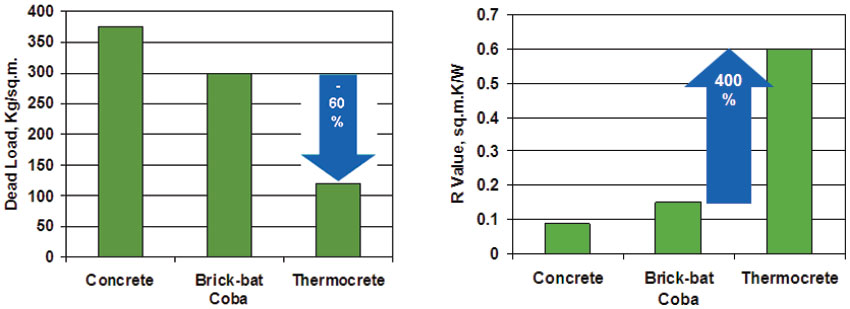
A comparative graph of "R-value" with the above insulation materials as compared to brickbat coba is shown here:
Slope Built-up
Thermocrete™A need is felt for a suitable material to replace brickbat coba for the purpose of making slope/fall on the flat roof slab for the purpose of water run-off and also for the protection of waterproofing and insulation layers.
Thermocrete™ is an excellent replacement for brickbat coba on a roof built-up due to its light weight, high thermal insulation, better compressive strength, low water absorption and ease of installation.

Thermocrete™ is site-batched light weight trowelable concrete using selective grades of expanded polystyrene beads (EPS) as thermal insulating aggregates. It combines the construction ease of concrete with the thermal insulation properties of EPS and can be used for a very wide range of application where lighter loads or thermal insulation or both are desired.
Comparitive charts for Dead Load & Thermal Resistance "R" for 150mm thick overlay.
Wall Insulation
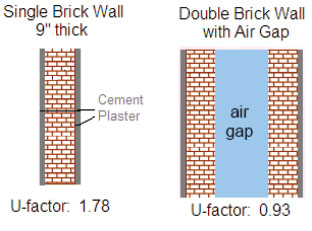
All these drawbacks are avoided by using "External Insulation & Finishing System" (EIFS) on the walls.
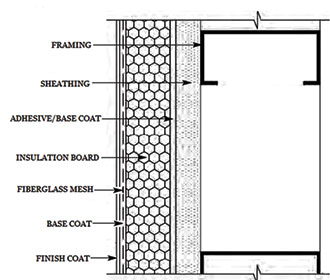
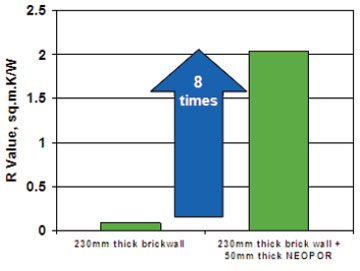
- SENERGY EIFS system consists of Neopor insulation board, adhesive for fixing insulation board to the substrate, anchoring system for fixing the reinforcing mesh in place over the insulation board and base coat which provide the mineral substrate for the application of the top coat. The top coat provides the long lasting aesthetics and finish to the system. Based on the insulation performance warranted, the type and thickness of insulation board is designed.
Sections of EIFS on a framed sheathing and on a concrete/plastered brick surface are as shown below EIFS offers the following benefits which are not offered/matched by other wall insulation methods. - EIFS has superior energy efficiency by reducing heat transmission and helps in reducing HVAC load.
- The adhesive coat, base coat & top finish coat are polymer based and provide high degree of water resistance to the wall.
- It can be applied to new & existing structures.
- External Location; Virtually Seamless – Reduced Air Infiltration
- Offers design flexibility, shapes, colors and textures
- Flexible and Lightweight Material
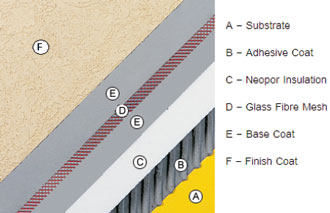
- Little Routine Maintenance
- It is the only solution for insulating existing buildings. Neopor Insulation Board: This high performance thermal insulation board is used in SENERGY EIFS.
- Contains Infrared absorbers/ deflectors
- 20% higher energy efficiency then EPS
- Flame retardant grade (B2)
- K value of 0.032 W/m.K
- Free of CFC, HCFC or HFC
Conclusion