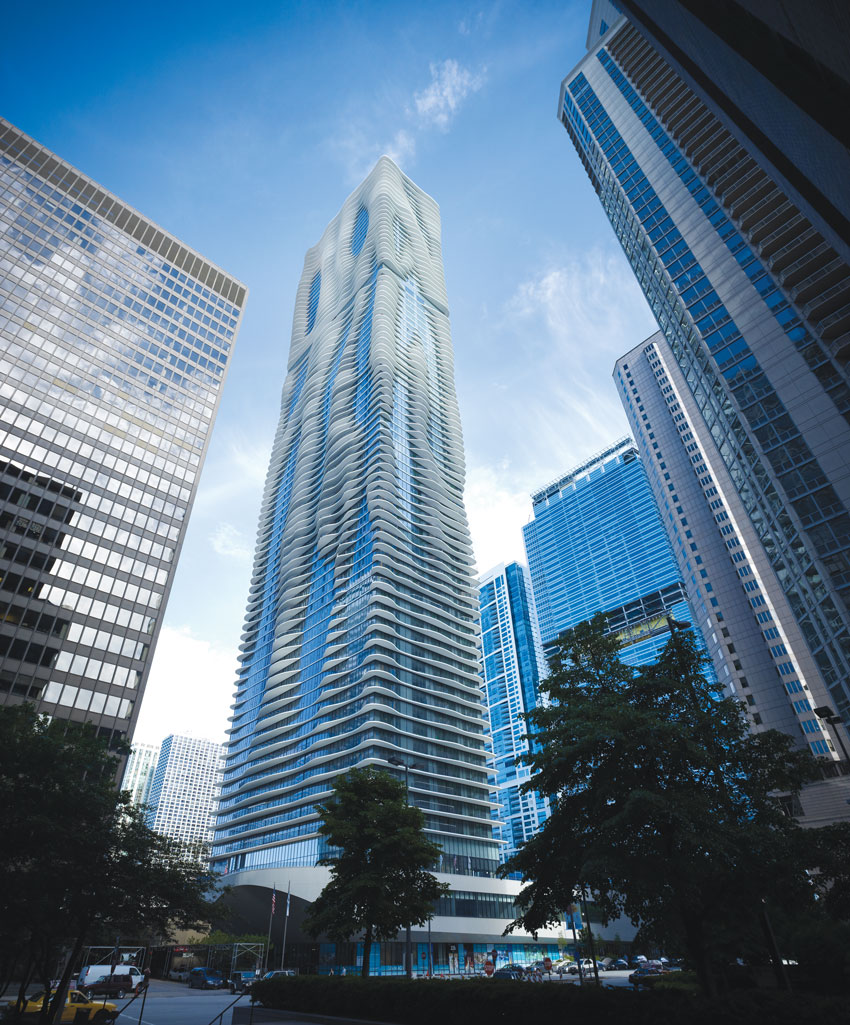
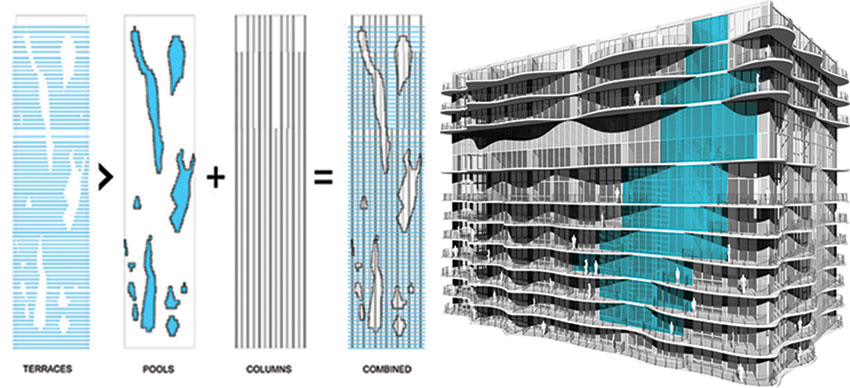
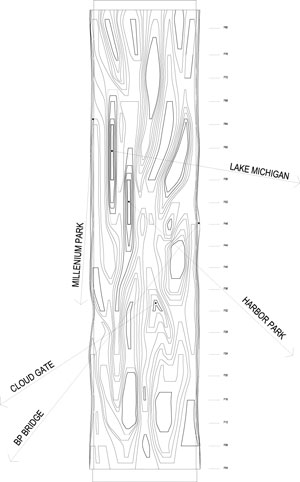

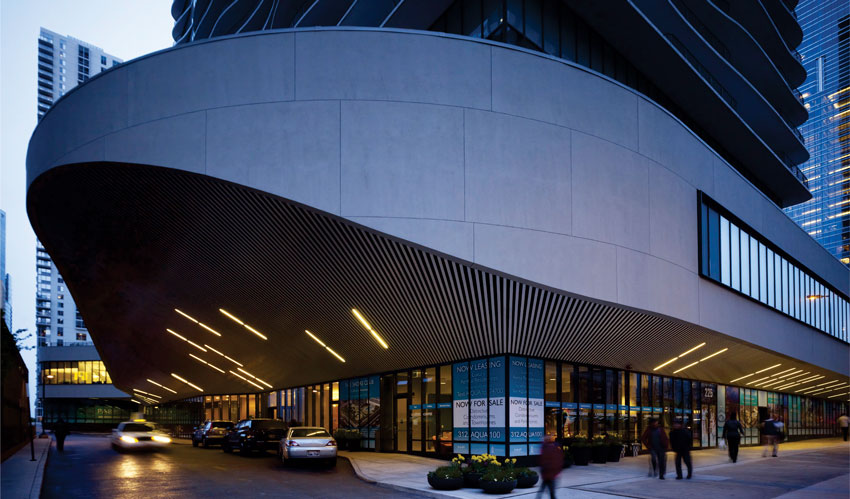
Located on the 200 block of North Columbus Drive, and surrounded by highrises, Aqua rises from a podium on the 179,946 square feet site near Millennium Park. The architect Jeanne Gang has given swirling architectonic form to this 1.9 million square feet structures' envelop while working with the building's rectangular footprint. As a mixed-use structure that contains 55,000 square feet (5,100 square meters) of retail and office space, in addition to 215 hotel rooms (floors 1-18), 476 rental residential units (floors 19-52), and 263 condominium units & Penthouses (floors 53-81), Aqua's entrances serve a variety of users and residents. Canopied walkways lead visitors to the building's main entrance while two grand public stairs bring pedestrians from Upper Columbus Drive down to a park at grade level, providing access to Chicago's downtown area and lakefront. The tower also connects to Chicago's extensive underground pedway system, linking users and residents to restaurants, retail, cultural activities and jobs in the Loop and on the Magnificent Mile. Additional consideration was made when designing the tower's garage exits below grade to minimize congestion at pedestrian levels. To further reduce traffic and confusion, the garage's three levels have different access points that correlate to the tower's specific uses and users.



Aqua Tower was recognized as a finalist in the 2010 CTBUH Awards Program. According to Mun Summ Wong, CTBUH 2010 Awards Juror, and WOHA Architects "The differential cantilevering balconies on Aqua transform a standardized glass box into a sublime amorphous form."

| Project at a Glimpse | |
| Location: | Chicago, IL (Chicago River Watershed) |
| Gross area: | 1,900,000 ft2 (176,516 m2) |
| Cost: | $475 million ($300 million, construction) |
| Completed: | 2010 |
| Program: | Hotel, apartments, condominiums, parking, retail, restaurants, offices, green roof terrace with outdoor pool, running track, and gardens |
| Architect: | Studio Gang Architects; Loewenberg Architects (architect of record) |
| Owner: | Magellan Development Group |
| Landscape architect: | Wolff Landscape Architecture |
| Environmental consultants: | Khatib and Associates (energy); Advance Mechanical Systems (geotechnical) |
| General contractor: | James McHugh Construction Company |
Sustainable Designs
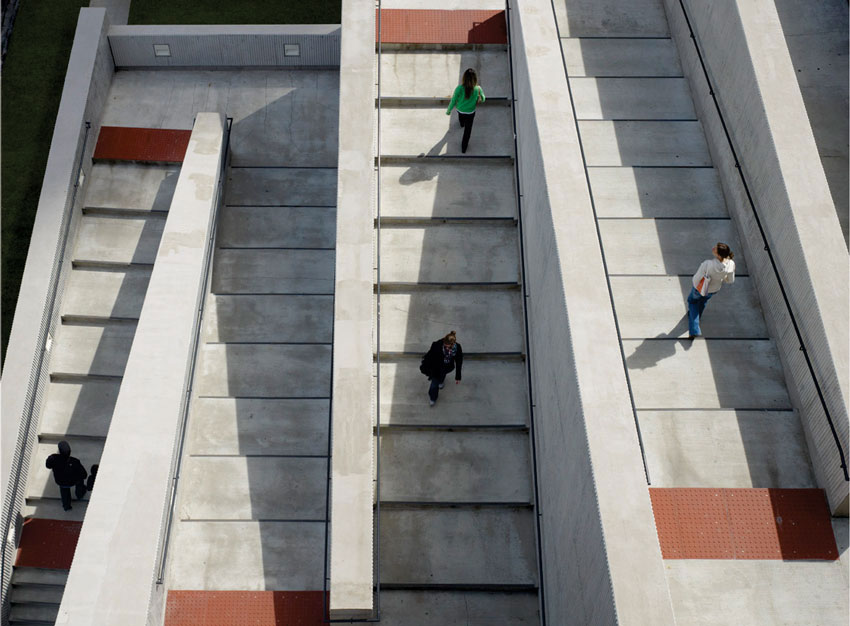
Sustainability was an important factor that was considered in Aqua's design. Among building's notable features is the green roof terrace atop its plinth-which at 80,000 sf is one of Chicago's largest-that contains an outdoor pool, running track, gardens, fire pits and yoga terrace. From below, Aqua's plinth navigates the site's complexity by spanning over pre-existing elements, such as an electrical substation, and by aligning with existing infrastructure, including an adjacent three-level roadway. The plinth physically connects pedestrian areas with stairs and elevators linking street level to park level and the lakefront.
The tower's east–west orientation maximizes its winter solar performance. Its balconies extend further on the southern façade to provide shading, reducing solar exposure in summer and allowing passive warming in winter.
In addition to low-E coatings on all glass, the design team modeled seasonal sun patterns to identify remaining areas of glass that needed higher performing glazing to increase energy efficiency throughout the tower. Glass on the east and south façades are reflective in areas without a protective balcony, while glass facing west has a tinted coating that improves its shading coefficient. In total, Aqua employs six different types of glass: clear, tinted, reflective, spandrel, fritted and translucent, the placement of which is determined by the orientation and function of interior space. Fritted glass is used and combined with handrail design to minimize bird strikes.

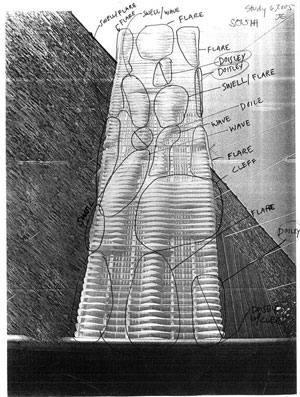
"Aqua Tower was shaped by an organic, site-specific design process. Rather than starting out with the goal of creating an icon, we let the climate and views shape the building, weaving it into its surroundings and treating the building and its environment as interconnected not separate. Even though it may appear to be formally expressive, it is equal parts data and imagination" –– Jeanne Gang, Design Principal Architect.
In addition, detailed wind tunnel studies were also done to confirm the performance of the structure under high winds. Initially, it was thought that a supplemental tuned mass damping system may be required to appropriately manage the effects of the wind on occupant comfort. However, during the testing, it was discovered that the undulating slab edges disrupted or "confused" the flow of wind around the tower, effectively reducing the wind demands, and this, combined with the effectiveness of the structural design, eliminated the need for a supplemental damping system.
Inside the dwelling units, the architects selected materials and equipment with sustainable features such as renewable and recyclable bamboo for the floors, plumbing fixtures including toilets, faucets, and showerheads that cut down on water use, plus Energy Star-rated appliances.









